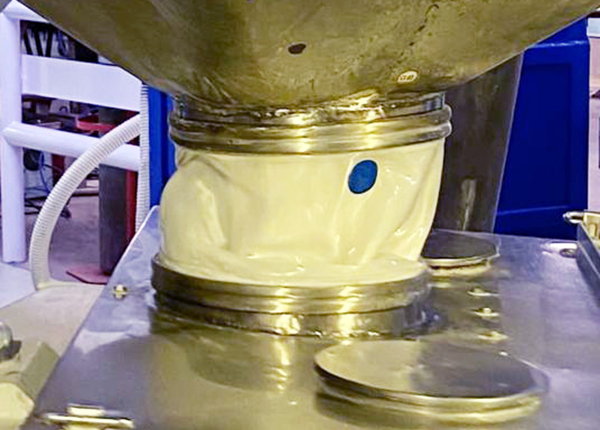
With more than 30 years of experience in the market, at Bikar we have cutting-edge technology to manufacture expansion joints. Our concern is continuous improvement. For this reason, we build loyalty through design and manufacturing, applying experience and innovation.
There are several keys or variables that we need to know from Bikar both to be able to design our solution and to advise on the best expansion joint, in case of doubt. Aspects as simple as knowing the type of fluid, the working/design pressure, and the working/design temperature will give us essential information to design our first solution.
In case of having more information, the answer will be complete. We would be talking about information on the exact movements to be supported, information on the installation of the line, fixed points and their locations, etc.
Depending on the design conditions indicated by the client, we will implement rubber, metal or fabric solutions. At Bikar we are capable of producing the 3 solutions.
1. Rubber expansion joints
Rubber expansion joints are characterized by their qualities of high resistance to corrosion, abrasion, absorption of movements, vibrations, noise, misalignment and stress. This type of expansion joints are mainly used to absorb movements, vibrations and stresses in piping systems with fluids at temperatures below 200ºC (39ºF) and normal pressures below 25 bar (362 psi).
In the same way, rubber expansion joints protect high-value equipment (pumps, valves, condensers, etc.) against thermal movements and mechanical stresses. We can design and produce special expansion joints for high pressures and movements on request.
We design rubber expansion joints following the recommendations of the FSA (Fluid Sealing Association), selecting the most appropriate elastomers for the bellows (EPDM, Viton, Hypalon, NBR, Neoprene, SBR…) and their reinforcements (Nylon and Kevlar) and dimensions ranging from DN 25(1”) to DN 4000 (160”). Flanges are available in a wide variety of materials (Carbon Steel, 316, 904, Super Duplex) and standards (DIN, ANSI, AWWA, JIS, BS).
2. Metal expansion joints
Metal expansion joints are the ideal solution for high performance piping systems with high temperatures and pressures.
They are mainly used in refineries, petrochemicals, power generation, steel mills, heating networks, desulfurization plants, shipbuilding and other industrial applications.
Our metal expansion joints absorb movement and stress in piping systems with fluids at temperatures up to 1200C (2200°F) and pressures up to 100 bar (1450 psi). Dimensions up to DN 3500 (140”). Main Materials: 321 ss, 316 ss, 304, 904, Duplex, Super Duplex, Monel, Inconel 625 and 800, Titanium. Compliance standard flanges.
The designs of our metal expansion joints are based on the requirements established by the EJMA standards (Expansion Joints Manufacturers Association of ANSI, the ASME Boiler and Pressure Vessel (Section VIII, Appendix 26), ASME B31.1 (Appendix X) and according to with the European directive for pressure equipment PED97/23/EC and with the standards EN 13445, EN 13480 and EN 14917. The calculations are carried out using software packages developed on the basis of the standards described above.
3. Fabric expansion joints
Fabric expansion joints are specially designed to offer high performance in piping systems with high temperatures and low pressures.
For this reason, fabric expansion joints are mainly used in boilers, ventilation circuits, industrial furnaces, cement plants, foundries, mining and paper mills.
This type of expansion joints are manufactured to simultaneously absorb movements in various directions, vibrations and avoid stresses in piping systems with gases, air or vapors at temperatures up to 1200°C (2200°F) and pressures below 0.35 kg/cm2 (5psi).
Fabric expansion joints provide high chemical resistance, minimal activation forces and reduced heat loss.
All our fabric expansion joints are designed under the FSA (Fluid Sealing Association) regulations, using PTFE laminates and other advanced materials for their manufacture in order to provide an optimal solution for the mechanical, chemical and thermal demands of the process.
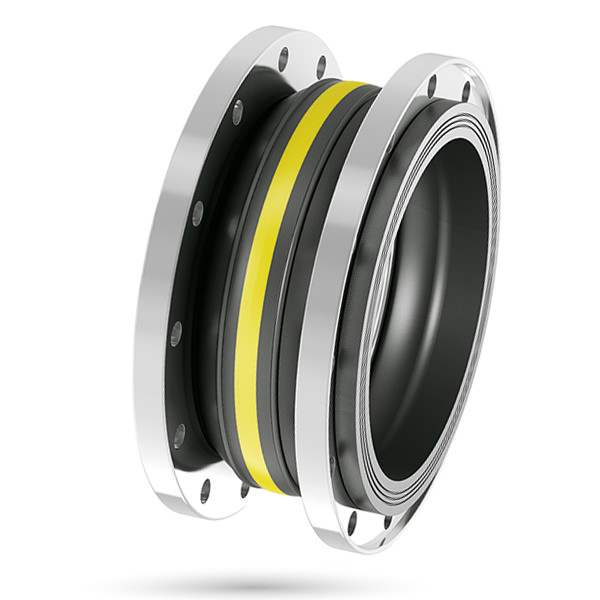



How to correctly choose the type of expansion joint
The determining factors are: the temperature of the internal fluid, the pressure of the internal fluid, what type of fluid is going to circulate and where the expansion joint is going to be placed. In summary: